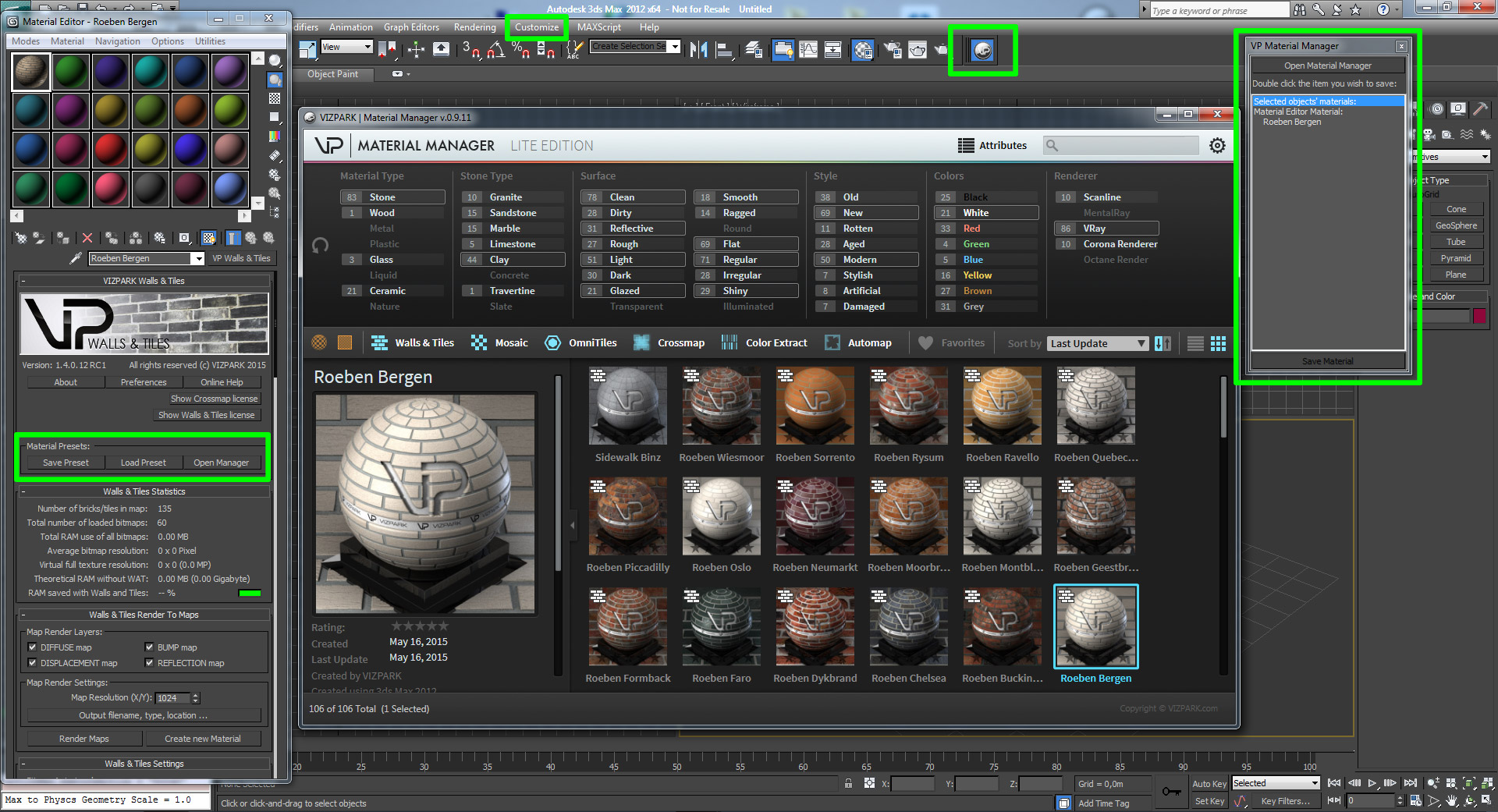
Middle clicking grabs a full stack of the item. Middle click dragging drops down full stacks. To load/unload all of an item, first pick up any item, then while holding it hover over one if the item stacks you want to load/unload all of and shift double click. Lets you specify a custom background for the sample slots, instead of the default checkers background. Click the file-assignment button to display a file dialog from which you can select the custom background. This can be any bitmap format supported by 3ds Max.

The Shading module covers:
- V-Ray Material – V-Ray material settings, and how to use them to simulate a wide range of real world materials.
- V-Ray SSS Materials – V-Ray FastSSS2 and V-Ray Skin materials, and how to use them tocreate translucent or sub-surface scattering materials.
- V-Ray 2-Sided Material – V-Ray 2-Sided material, and how to use it to create thin translucent materials such as fabric or paper.
- V-Ray Blend and Bump Materials – How to create more complex materials.
- Random Color Techniques – How the V-Ray Multi Sub texture and the V-Ray User Color node can generate random colors in a shading network.
Glass transmission fake caustic on floor plane (shadow_matte)
Arnold is a unidirectional path tracer and therefore realistic caustics can be expensive to render. This is because caustic effects create a lot of noise and require very high sampling values, which can lead to long rendering times. This tutorial shows how to create a fake caustic effect that is far cheaper to render but still looks convincing. It uses a combination of the ray_switch, standard_surface, and facing_ratio shaders and assigns them to the object that emits caustics. A shadow_matte shader is then assigned to the floors standard_surface.emission attribute that gives the caustic effect.
It should be noted that the technique in this tutorial is not physically correct and does not demonstrate the result of a physically correct caustic effect. However, in most cases, the rendered results should be sufficient to fool the eye. Thanks to Slava Sych for his help with this tutorial.
| The shader can be downloaded here. |
|---|
Information about rendering true caustics can be found here.
Scene Setup and Lighting
- Place the object that you want to emit caustics from in the scene. Create a camera and set the desired position. Create a floor plane to sit under the object.
- Create a distant_light (directional). Increase its exposure to 3, angle to 3 and samples to 3.
Camera Glass Shader
- Next, create a standard_surface shader. Rename it to something like CamGlass and assign to the object. This will be the shader that is visible to camera rays. Change the following parameters:
specular_IOR: 1.550
transmission_weight: 1.0
coat_weight: 1.0
coat_roughness: 0.1
coat_IOR: 1.550 Enable transmit_aov so that you can render out separate caustic AOVs.
Shadow Glass Shader
- Next, create a new standard_surface shader and rename it ShadowGlass. Change the following parameters:
transmission_weight: 1.0
Enable transmit_aov
Facing Ratio
Create a facing_ratio shader and connect its output to transmission_weight of the ShadowGlass shader.
The facing_ratio parameters used will be dependent on the particular object that you are using and therefore may need to be adjusted.
Bias: 0.136Gain: 0.619
Enable Linear
Enable Invert
Ray Switch Shader
Next, create a ray_switch shader and assign it to the object. Rename it to GlassMat. This will be used to tell Arnold which rays to use when rendering the glass object.
- Connect the CamGlass shader output to the camera, diffuse_reflection, diffuse_transmission, specular_reflection, and transmission parameters of the GlassMat (Ray Switch) shader.
- Connect the ShadowGlass shader output to the shadow parameter of the GlassMat shader.
Ray Switch shader
Floor Plane Shader
- Create a second standard_surface shader and rename it to FloorMat. Assign it to the floor plane geometry. Change the following parameters:
Specular Roughness: 0.2 Emission: 1
ShadowMatte -> Range -> ColorCorrect -> Standard Surface
- Create a shadow_matte, range and color_correct shaders.
- Connect the shadow_matte output to the range input. Connect the range output to the input of the color_correct and connect the color_correct output
to the emission_color of the FloorMat shader.
Shadow Matte:
The Shading module covers:
- V-Ray Material – V-Ray material settings, and how to use them to simulate a wide range of real world materials.
- V-Ray SSS Materials – V-Ray FastSSS2 and V-Ray Skin materials, and how to use them tocreate translucent or sub-surface scattering materials.
- V-Ray 2-Sided Material – V-Ray 2-Sided material, and how to use it to create thin translucent materials such as fabric or paper.
- V-Ray Blend and Bump Materials – How to create more complex materials.
- Random Color Techniques – How the V-Ray Multi Sub texture and the V-Ray User Color node can generate random colors in a shading network.
Glass transmission fake caustic on floor plane (shadow_matte)
Arnold is a unidirectional path tracer and therefore realistic caustics can be expensive to render. This is because caustic effects create a lot of noise and require very high sampling values, which can lead to long rendering times. This tutorial shows how to create a fake caustic effect that is far cheaper to render but still looks convincing. It uses a combination of the ray_switch, standard_surface, and facing_ratio shaders and assigns them to the object that emits caustics. A shadow_matte shader is then assigned to the floors standard_surface.emission attribute that gives the caustic effect.
It should be noted that the technique in this tutorial is not physically correct and does not demonstrate the result of a physically correct caustic effect. However, in most cases, the rendered results should be sufficient to fool the eye. Thanks to Slava Sych for his help with this tutorial.
| The shader can be downloaded here. |
|---|
Information about rendering true caustics can be found here.
Scene Setup and Lighting
- Place the object that you want to emit caustics from in the scene. Create a camera and set the desired position. Create a floor plane to sit under the object.
- Create a distant_light (directional). Increase its exposure to 3, angle to 3 and samples to 3.
Camera Glass Shader
- Next, create a standard_surface shader. Rename it to something like CamGlass and assign to the object. This will be the shader that is visible to camera rays. Change the following parameters:
specular_IOR: 1.550
transmission_weight: 1.0
coat_weight: 1.0
coat_roughness: 0.1
coat_IOR: 1.550 Enable transmit_aov so that you can render out separate caustic AOVs.
Shadow Glass Shader
- Next, create a new standard_surface shader and rename it ShadowGlass. Change the following parameters:
transmission_weight: 1.0
Enable transmit_aov
Facing Ratio
Create a facing_ratio shader and connect its output to transmission_weight of the ShadowGlass shader.
The facing_ratio parameters used will be dependent on the particular object that you are using and therefore may need to be adjusted.
Bias: 0.136Gain: 0.619
Enable Linear
Enable Invert
Ray Switch Shader
Next, create a ray_switch shader and assign it to the object. Rename it to GlassMat. This will be used to tell Arnold which rays to use when rendering the glass object.
- Connect the CamGlass shader output to the camera, diffuse_reflection, diffuse_transmission, specular_reflection, and transmission parameters of the GlassMat (Ray Switch) shader.
- Connect the ShadowGlass shader output to the shadow parameter of the GlassMat shader.
Ray Switch shader
Floor Plane Shader
- Create a second standard_surface shader and rename it to FloorMat. Assign it to the floor plane geometry. Change the following parameters:
Specular Roughness: 0.2 Emission: 1
ShadowMatte -> Range -> ColorCorrect -> Standard Surface
- Create a shadow_matte, range and color_correct shaders.
- Connect the shadow_matte output to the range input. Connect the range output to the input of the color_correct and connect the color_correct output
to the emission_color of the FloorMat shader.
Shadow Matte:
Set Background to Background Color.Background Color: 0.0 0.0 0.0
Shadow Color: 1.0 1.0 1.0
Shadow Opacity 1.0
Backlighting: 0.0
Enable: Alpha Mask
Diffuse Intensity: 0.0
Range:
Enable smoothstep
ColorCorrect:
shadow_matte -> range -> color_correct -> FloorMat (standard_surface)
Skydome Light
When using a skydome_light, there are some steps required to not break the caustic effect.
How To Make More Material Slots In 3ds Max
- Create a skydome_light, connect an HDR map to its color parameter and set the following parameters:
This light is to be used for lighting the Glass material itself and is notrequired for the caustic effect. You may need to break light linking between the skydome_light and the floor plane otherwise the caustic effect may not be visible properly. If you need lighting from a background with HDRI, try creating a second skydome_light and break its light linking with the glass object.
Scene setup with skydome_light. Glass object is better lit.
Render Layers for Compositing
How To Create More Material Slots 3ds Max Games
Now the scene is ready to set up render layers for AOV compositing. These can be used to fine-tune the caustics, add dispersion effects, etc.
Increasing the specular_ray_depth will create more reflective bounces in the glass object and give a more realistic result. Note that increasing this value will increase render times.
Glass shader (left). Floor shader (right).